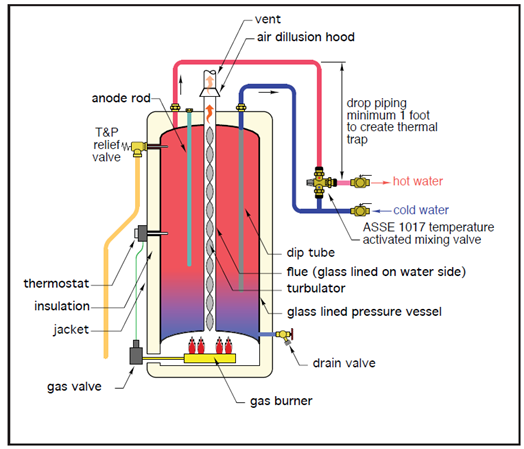
Ever wondered what makes your water heater tick? It's more than just a metal tank! Understanding the inner workings of your water heater can help you troubleshoot issues, make informed decisions about maintenance, and even extend its lifespan. Let's break down the key water heater components and what they do.
The Tank: The Heart of the System
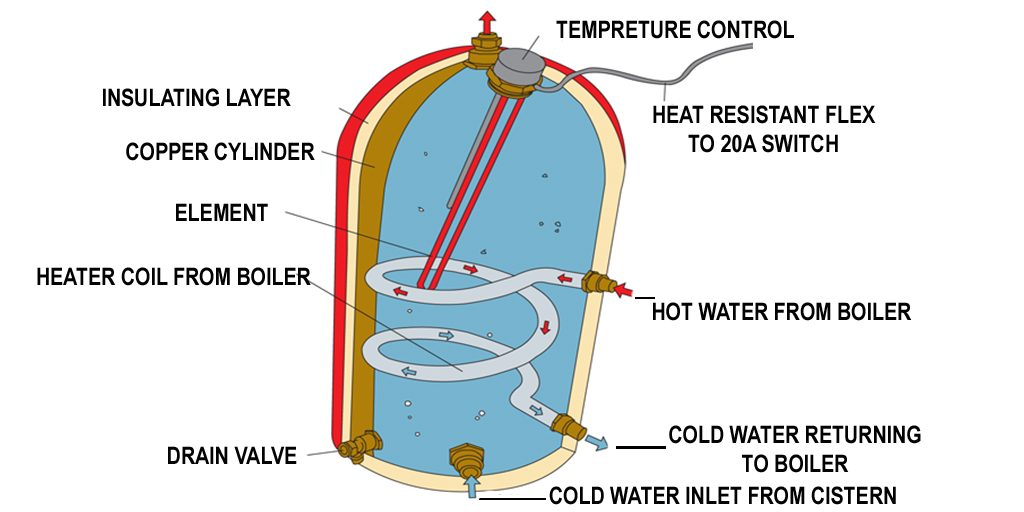
The most visible part of a water heater is the tank. This is where the water is stored and heated. Tanks come in various sizes, typically measured in gallons, to accommodate different household needs. Inside, the tank is usually lined with a protective material, such as glass or porcelain, to prevent corrosion.
Heating Elements: The Power Source
For electric water heaters, heating elements are crucial. These are essentially resistors that convert electrical energy into heat. They're submerged in the water and raise its temperature. Most electric heaters have two elements: an upper and a lower one. Gas water heaters, on the other hand, use a burner located at the bottom of the tank to heat the water.
- Electric Heating Elements: Convert electricity to heat.
- Gas Burner: Uses natural gas or propane to heat the water.

Thermostat: Temperature Control
The thermostat is the brain of the water heater, responsible for regulating the water temperature. It senses the water temperature and turns the heating elements or burner on or off as needed to maintain the desired setting. Adjusting the thermostat allows you to control how hot your water gets.
Dip Tube: Delivering Cold Water
The dip tube is a long pipe that extends from the top of the tank to near the bottom. Its job is to deliver cold water into the tank. This ensures that the incoming cold water doesn't immediately mix with the hot water at the top, allowing for more efficient heating.
Anode Rod: Corrosion Protection
The anode rod is a sacrificial rod, usually made of magnesium or aluminum, that helps prevent corrosion of the tank. It attracts corrosive elements in the water, sacrificing itself to protect the tank lining. Regular inspection and replacement of the anode rod can significantly extend the life of your water heater.
Pressure Relief Valve: Safety First
The pressure relief valve (also known as the temperature and pressure relief valve or T&P valve) is a critical safety component. It's designed to release excess pressure or temperature from the tank, preventing potential explosions. If the pressure or temperature exceeds safe levels, the valve will open and release water.
Drain Valve: Maintenance Made Easy

The drain valve is located at the bottom of the tank and is used to drain water for maintenance or to flush sediment. Regularly draining your water heater helps prevent sediment buildup, which can reduce efficiency and shorten the lifespan of the heater.
Insulation: Keeping the Heat In
Most modern water heaters come with built-in insulation to minimize heat loss. This helps maintain the water temperature and reduces energy consumption. Some older models may benefit from additional insulation blankets.
Flue or Vent: Exhausting Gases
For gas water heaters, the flue or vent is essential for safely exhausting combustion gases outside the home. Proper venting prevents the buildup of dangerous gases like carbon monoxide.
Understanding these water heater components allows you to better maintain your system, troubleshoot minor issues, and make informed decisions when it's time for repairs or replacement. Regular maintenance, such as flushing the tank and inspecting the anode rod, can significantly extend the life of your water heater and ensure you always have hot water when you need it.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.