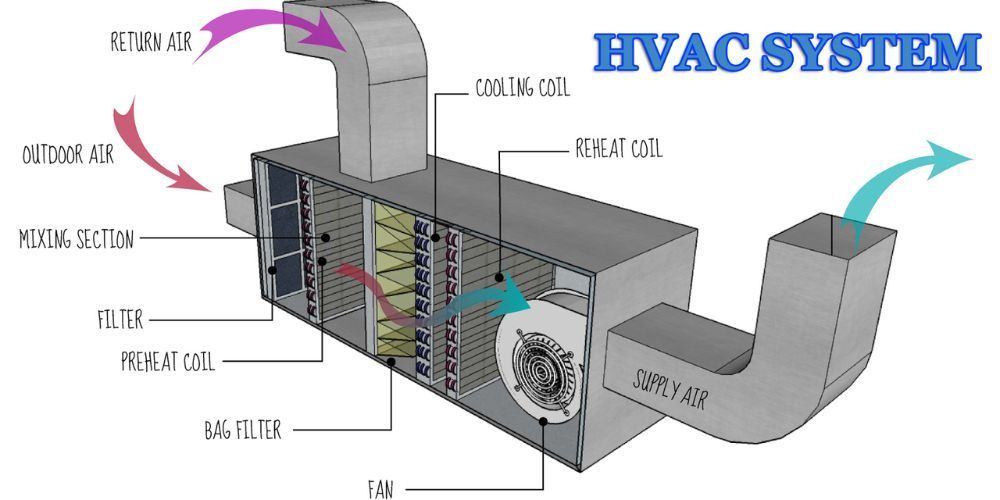
Introduction: Why Reliable Air Conditioning Service Matters
When the summer sun turns your home into an oven, your air conditioner becomes more than a luxury—it’s a lifeline. But here’s the thing: not all air conditioning services are created equal. A “quick fix” from an unreliable company can cost you more in the long run, both financially and in comfort. That’s why choosing a reliable air conditioning service is essential.
Think about it—would you trust just anyone with your car’s engine? The same principle applies to your AC system. It’s one of the most critical investments in your home. A properly serviced air conditioner doesn’t just keep you cool; it improves indoor air quality, reduces energy bills, and extends the lifespan of your unit.
Unfortunately, many homeowners wait until their system breaks down before calling for help. By then, minor issues may have snowballed into major (and costly) repairs. Reliable service ensures that problems are caught early, maintenance is done regularly, and you’re not left sweating in the middle of July.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about finding and maintaining a trustworthy air conditioning service provider. From spotting warning signs of trouble to choosing the right company, this article will give you the tools to keep your home cool, efficient, and stress-free year-round.
Understanding the Role of Air Conditioning in Modern Homes
Importance of Indoor Comfort
Air conditioning isn’t just about keeping your home cool. It’s about creating an environment where you and your family can live, work, and relax comfortably. In fact, studies show that room temperature has a direct impact on mood, concentration, and productivity. That’s why offices, schools, and homes alike depend on air conditioning systems.
Imagine trying to sleep through a heatwave without AC. Not only does it disrupt rest, but poor sleep also affects your overall health. Reliable air conditioning service ensures your unit works when you need it most, giving you the comfort you deserve.
Impact on Health and Productivity
Beyond comfort, air conditioning plays a critical role in maintaining healthy indoor air quality. Modern AC systems filter out dust, allergens, and pollutants, reducing the risk of respiratory problems. For individuals with asthma or allergies, a well-maintained system is a must.
Productivity also takes a hit when your AC is on the fritz. Overheated environments lead to fatigue and irritability, making it nearly impossible to focus. That’s why businesses invest heavily in HVAC maintenance—because employee comfort directly impacts performance.
Reliable AC service goes beyond cooling. It’s about protecting your health, boosting productivity, and ensuring that every breath of air in your home or office is clean and refreshing.
Signs Your Air Conditioner Needs Professional Service
Common Red Flags
Like a car, your air conditioner often gives you warning signs before it breaks down completely. The trick is knowing what to look for. Some of the most common red flags include:
-
Weak airflow: If your vents feel more like a whisper than a breeze, there’s likely a blockage or failing motor.
-
Unusual noises: Grinding, banging, or squealing sounds usually mean something is loose or damaged inside.
-
Bad odors: Musty smells often indicate mold, while burning odors can signal electrical issues.
-
Higher energy bills: A sudden spike in your utility bill usually means your AC is working harder than it should.
When to Call an Expert Immediately
Some issues can wait until your next maintenance appointment, but others require immediate attention. Call a professional right away if:
-
Your AC blows warm air instead of cold.
-
The system won’t turn on at all.
-
You notice water leaks or refrigerant puddles.
-
The circuit breaker keeps tripping when your AC runs.
Waiting too long can turn a simple fix into a major repair—or even a full system replacement. A reliable air conditioning service provider will respond quickly, diagnose the issue, and get your home back to comfortable in no time.
Key Benefits of Choosing a Reliable AC Service Provider
Consistent Comfort and Peace of Mind
When you hire a trustworthy AC service company, you’re not just paying for repairs—you’re buying peace of mind. You can rest easy knowing that your unit is being handled by trained professionals who understand every nut and bolt of the system. That means fewer unexpected breakdowns and consistent comfort throughout the year.
Energy Savings and Cost Efficiency
A poorly maintained AC system can eat up electricity like a sponge. Reliable service providers fine-tune your unit to run efficiently, lowering energy consumption and cutting monthly bills. Over time, these savings can easily outweigh the cost of routine service.
Extended Equipment Lifespan
Just like oil changes keep your car running longer, regular AC service extends the life of your cooling system. Instead of replacing your unit after 8 years, you might stretch it to 12–15 years with proper care. That’s thousands of dollars saved simply by scheduling reliable maintenance.
The real benefit? You’ll avoid those dreaded mid-summer breakdowns when repair companies are fully booked and you’re left waiting in a sweltering home. Reliable service means you’re always ahead of the curve.
Different Types of Air Conditioning Services Explained
Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance is the backbone of reliable AC service. This typically includes cleaning coils, replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting electrical components. It’s a preventative approach designed to catch small problems before they spiral into big ones.
Repair Services
No matter how well you maintain your system, breakdowns happen. Reliable AC repair services focus on diagnosing the issue quickly and fixing it right the first time. Whether it’s a faulty compressor, a clogged drain line, or a refrigerant leak, skilled technicians ensure minimal downtime.
Installation & Replacement
If your unit is more than 10–15 years old or constantly breaking down, replacement might be the smarter choice. Reliable service companies guide you through the process—from choosing the right size unit for your home to ensuring proper installation. This guarantees efficiency and maximizes comfort.
Emergency Services
Nothing’s worse than an AC breakdown during a heatwave. That’s why many top companies offer 24/7 emergency services. A reliable provider responds quickly, often within hours, to restore your comfort and prevent further damage to your system.
How to Choose the Right Air Conditioning Service Company
Reputation and Reviews
In today’s digital age, reputation is everything. Before trusting a company with your home’s cooling system, check their online reviews. Platforms like Google, Yelp, and Better Business Bureau offer genuine insights into customer satisfaction. Look for consistent positive feedback about punctuality, professionalism, and service quality. A company with years of strong reviews is far more reliable than one with little to no online presence.
Word-of-mouth recommendations are equally powerful. Ask your neighbors, friends, or colleagues about their experiences. Reliable service providers earn repeat business because they deliver consistent results. If you hear the same name pop up often, that’s usually a good sign.
Certifications and Licensing
Not all technicians are created equal. Reliable AC service companies employ certified professionals who meet industry standards. Certifications from organizations like NATE (North American Technician Excellence) demonstrate expertise in handling HVAC systems.
Additionally, make sure the company holds proper state or local licenses. This ensures they comply with safety codes and regulations. Licensed professionals are also more likely to carry insurance, protecting you from liability in case of accidents or damage.
Service Guarantees and Warranties
A trustworthy company stands behind its work. Service guarantees give you confidence that if something goes wrong after the repair or installation, they’ll fix it at no extra cost. Warranties on parts and labor protect your investment and show that the company takes pride in its craftsmanship.
When choosing a provider, ask about their warranty policy. Do they offer coverage on both equipment and labor? Do they provide written guarantees? The best companies are transparent and confident in the quality of their work.
The Cost of Air Conditioning Services: What to Expect
Maintenance Costs
Routine maintenance is generally the most affordable service, and it saves you money in the long run. Expect to pay between $75 and $200 for a standard tune-up, which usually includes filter replacement, coil cleaning, and system inspection. Some companies offer yearly maintenance plans at discounted rates, ensuring your AC stays in peak condition without breaking the bank.
Repair Costs
Repair costs vary widely depending on the issue. Minor fixes, such as thermostat calibration or capacitor replacement, may cost under $200. Larger repairs, like a refrigerant leak or compressor failure, can climb into the thousands. Reliable companies provide upfront estimates so you’re not blindsided by the final bill.
Replacement and Installation Costs
If your AC system is outdated, replacing it is often more cost-effective than constant repairs. A standard central air conditioner replacement typically ranges from $3,000 to $7,000, depending on unit size and efficiency. High-efficiency or advanced systems may cost more but deliver significant energy savings over time.
Balancing Cost and Value
While it’s tempting to choose the cheapest option, reliable service is about long-term value. A low-cost “fix” might lead to repeat breakdowns, costing you more overall. The best providers balance affordability with quality, ensuring you get lasting results without unnecessary expenses.
DIY AC Maintenance Tips Every Homeowner Should Know
Cleaning and Filter Replacement
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to maintain your AC is regular filter replacement. Dirty filters block airflow, forcing your system to work harder and reducing efficiency. Replace filters every 1–3 months, especially during heavy use in summer.
Additionally, keep your outdoor unit free of debris. Leaves, grass, and dirt can clog the condenser coil, reducing performance. A gentle rinse with a garden hose is usually enough to keep it clean.
Checking Airflow and Vents
Blocked vents can create uneven cooling and strain your system. Make sure all vents are open and free of furniture or drapes. Poor airflow may also indicate a clogged duct, which requires professional cleaning.
Thermostat Management
A programmable or smart thermostat helps maximize efficiency. Set your thermostat a few degrees higher when you’re away and lower it only when you’re home. This reduces strain on your system and lowers energy bills.
When to Call in a Professional
While DIY maintenance goes a long way, it doesn’t replace professional service. Annual inspections are essential to check refrigerant levels, electrical connections, and system performance. Think of it as taking your car for a tune-up—you handle the basics, but the experts catch what you can’t.
The Role of Technology in Modern Air Conditioning Service
Smart Thermostats
Today’s air conditioning services often include integrating smart thermostats. These devices learn your schedule and adjust cooling patterns automatically, saving energy without sacrificing comfort. Many can be controlled remotely via smartphone apps, giving you full control even when you’re away.
Energy-Efficient Systems
Newer AC models are far more efficient than older ones. Look for units with ENERGY STAR certification, which meet government standards for energy efficiency. These systems may cost more upfront but significantly reduce monthly bills and environmental impact.
Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics
Some HVAC companies now offer remote system monitoring. Sensors installed in your AC track performance and send alerts when issues arise. This allows technicians to diagnose problems before they become emergencies, often reducing repair costs.
The Future of AC Technology
As technology advances, we can expect even smarter cooling systems. Artificial intelligence is already being tested in HVAC systems, allowing them to adjust in real-time based on occupancy and outdoor weather. Reliable service providers stay ahead of these trends, ensuring customers benefit from the latest innovations.
Seasonal AC Care: Preparing for Summer and Winter
Pre-Summer Checklist
Before the first heatwave hits, prepare your AC system with these steps:
-
Replace or clean filters.
-
Check thermostat calibration.
-
Clean outdoor condenser coils.
-
Ensure proper airflow from vents.
-
Schedule a professional inspection.
Starting the summer with a well-maintained system prevents breakdowns during peak demand and ensures maximum efficiency.
Winterization Steps
Even if you don’t use your AC in winter, it still needs care. Covering the outdoor unit protects it from snow, ice, and debris. Disconnecting power prevents accidental activation during freezing temperatures. Some homeowners even opt for a light maintenance check to ensure their system is ready for the next season.
Year-Round Peace of Mind
Seasonal preparation ensures your AC isn’t just reactive but proactive. Instead of waiting for problems, you’re staying ahead, which saves both money and stress. Reliable service providers often offer seasonal maintenance packages to make this process seamless.
Commercial vs. Residential Air Conditioning Services
Key Differences in Approach
While the goal of both residential and commercial air conditioning is to maintain comfort, the scale and complexity are entirely different. Residential systems typically cool smaller spaces with simpler ductwork and require less energy. On the other hand, commercial AC systems are designed for larger buildings, multiple floors, and higher occupancy rates. They often involve more advanced zoning systems, rooftop units, and extensive ventilation networks.
Another major difference lies in operating hours. Residential systems usually run during the day or evening, while commercial systems often operate continuously, especially in businesses that stay open late or around the clock. This means commercial systems demand more frequent and specialized maintenance.
Common Challenges
-
Residential Challenges: Homeowners often face clogged filters, thermostat malfunctions, and refrigerant leaks. While these issues are manageable, they still require reliable service to prevent escalating into larger problems.
-
Commercial Challenges: Businesses face issues like uneven cooling across large spaces, equipment failures that disrupt productivity, and higher energy costs. Because downtime directly impacts operations, reliability and quick response times are critical.
Reliable service providers specialize in both residential and commercial solutions, tailoring their approach to the specific demands of each environment.
Emergency AC Services: Why Reliability Matters Most
Quick Response Times
Nothing tests the reliability of an AC service provider more than an emergency. Imagine your AC failing in the middle of a scorching heatwave or during a busy workday in a crowded office. In such cases, response time is everything. The best companies offer 24/7 emergency services, ensuring a technician is dispatched immediately to restore comfort.
Avoiding Breakdowns During Heatwaves
Most AC emergencies happen during peak summer when systems are pushed to their limits. Reliable service companies don’t just fix the issue—they ensure the problem doesn’t return. By carrying common parts and tools, technicians can often resolve the issue in a single visit, avoiding repeat downtime.
Peace of Mind in Urgent Situations
Emergencies are stressful enough without worrying about whether your service provider will show up. Choosing a reliable AC company guarantees that even in the worst situations, you won’t be left sweating it out for days. This level of reliability is invaluable, especially for families with children, elderly residents, or businesses that depend on a comfortable environment.
Environmental Impact of Air Conditioning Services
Eco-Friendly AC Options
Air conditioning has a reputation for being energy-hungry, but modern systems are changing that. Eco-friendly AC units use advanced refrigerants that minimize environmental impact and are designed to run more efficiently. These systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions and lower your carbon footprint.
Energy-Efficient Practices
Reliable service providers don’t just install new units; they also help homeowners and businesses adopt energy-efficient practices. From recommending programmable thermostats to sealing duct leaks, these steps reduce energy consumption without compromising comfort.
Sustainable Future for Cooling
The HVAC industry is rapidly evolving with stricter energy regulations and greener technologies. Companies that prioritize eco-friendly solutions not only help the planet but also save customers money in the long run. Choosing a reliable AC service with a focus on sustainability ensures you’re contributing to a cleaner, healthier environment.
Future of Air Conditioning Services: Trends to Watch
Green HVAC Solutions
With rising energy costs and growing awareness of climate change, green HVAC solutions are becoming mainstream. Expect to see more solar-powered cooling systems, energy recovery ventilators, and advanced refrigerants that are safer for the environment.
AI and Smart Cooling Systems
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the HVAC industry. AI-powered systems can learn your usage patterns, adjust cooling automatically, and even predict maintenance needs before a failure occurs. This not only improves comfort but also maximizes energy efficiency.
Integration with Smart Homes and Businesses
As smart home technology continues to evolve, air conditioning systems are increasingly integrated with other devices. Imagine your AC working in harmony with lighting, blinds, and security systems for a fully automated and energy-efficient home. Reliable service providers who stay updated on these trends will be best positioned to serve future customer needs.
Conclusion: Ensuring Year-Round Comfort with Reliable AC Service
Choosing a reliable air conditioning service isn’t just about fixing a broken unit—it’s about protecting your comfort, health, and wallet. From routine maintenance to emergency repairs, the right provider ensures your AC system runs smoothly and efficiently year after year.
Reliable service means fewer breakdowns, lower energy bills, and a longer system lifespan. It also means peace of mind, knowing that no matter the season or situation, your home or business will stay cool and comfortable.
As technology and environmental standards evolve, the importance of partnering with a trustworthy AC company will only grow. So, whether you’re preparing for summer, replacing an old unit, or dealing with an urgent breakdown, remember this: reliability isn’t optional—it’s essential.
FAQs
1. How often should I schedule AC maintenance?
At least once a year, preferably before summer. For heavy usage, twice a year (spring and fall) is recommended.
2. What’s the average lifespan of an air conditioner?
With regular maintenance, most central AC units last 12–15 years.
3. Can I handle AC repairs on my own?
Basic tasks like replacing filters are DIY-friendly, but complex issues like refrigerant leaks or electrical problems require professional service.
4. What’s the most energy-efficient way to use my AC?
Use a programmable thermostat, maintain proper insulation, and schedule routine service to keep your system efficient.
5. How do I know if my AC needs replacement instead of repair?
If your system is over 10–15 years old, requires frequent repairs, or causes high energy bills, replacement is often the smarter choice.
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)